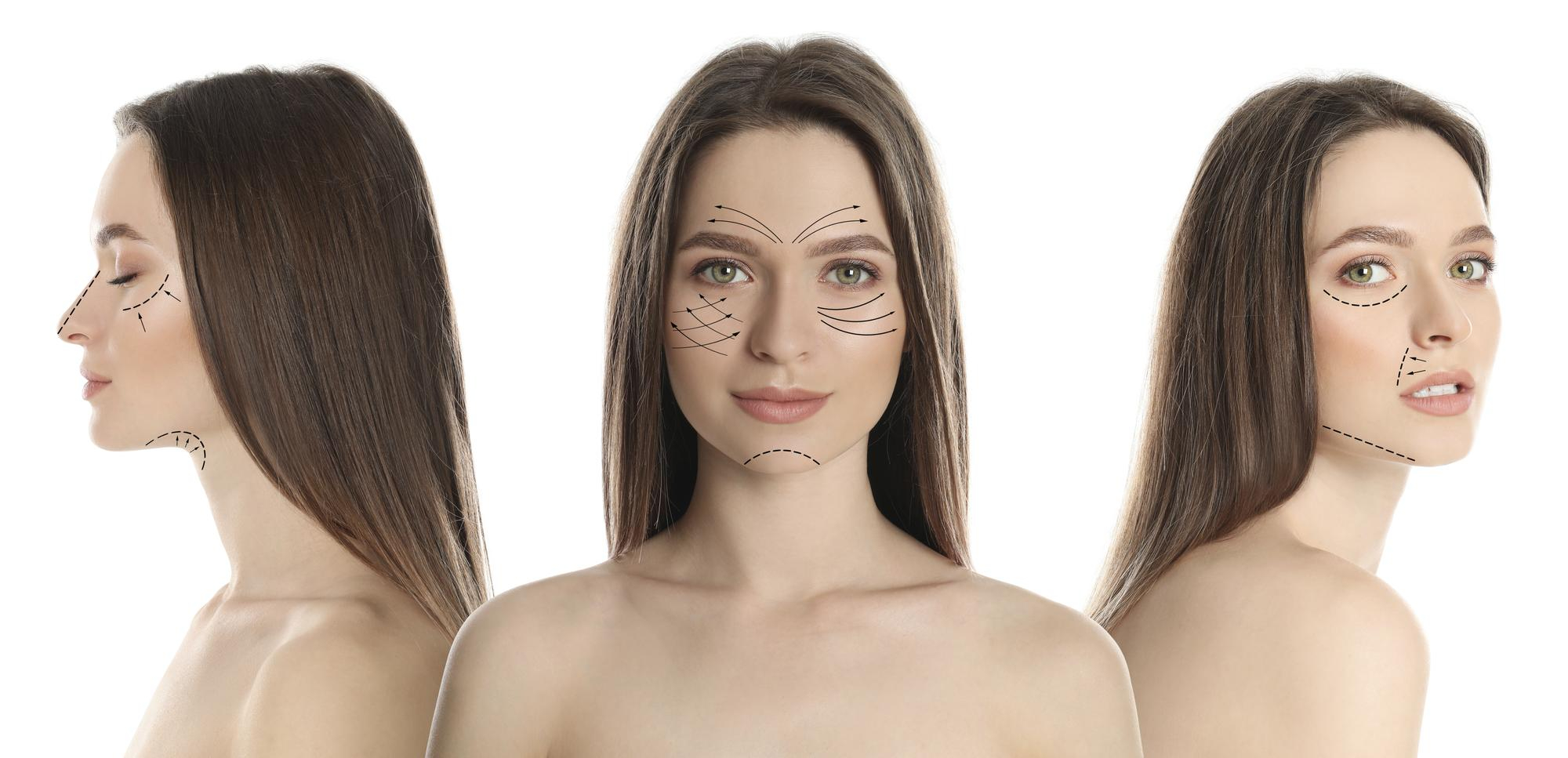
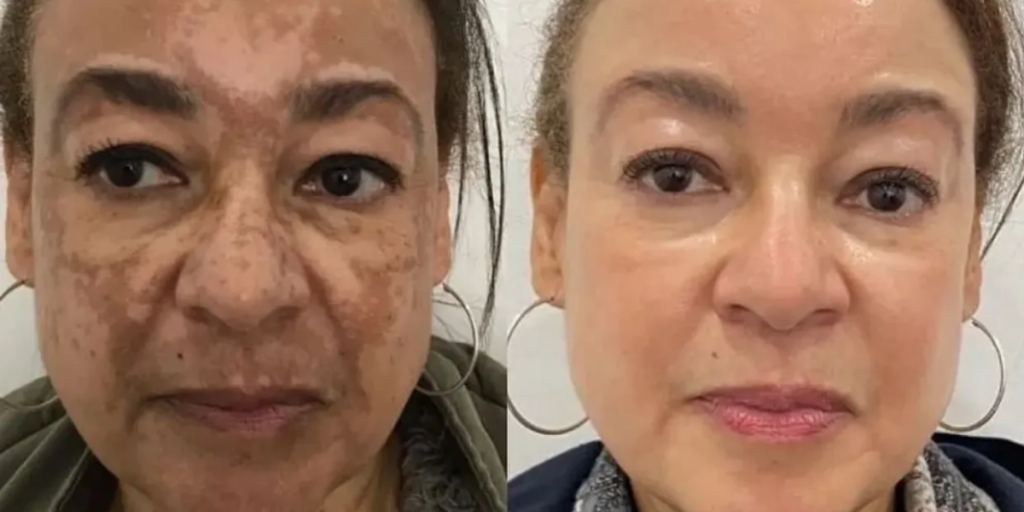
Chemical Peel for Pigmentation: What Really Works for Dark Spots, Melasma, and Eye Circles
A competent chemical peel for Pigmentation may be a life-changer in case you are struggling with an unyielding discoloration. Peels, whether to remove the traces of acne to melasma, exfoliate the dead, flattened skin and dislodge younger, fresher cells to the surface. This tutorial will take you through the mechanism of action of a chemical peel to treat pigmentation, which peels are appropriate to various issues, expectations, and safety, particularly in people with deeper pigmentation.
What is a chemical peel and its effect on pigment?
A chemical peel for Pigmentation involves the use of a controlled solution (mostly acids) to loosen the attachments between dead skin cells.
This process:
– Accelerates the rate of cells turning over faster so pigmented cells are shed at a higher rate.
– Enhances the feel and hue through overlaying the topmost layers.
– Helps erase sun-burns or acne or hormonal blotches.
– Increases the action penetration of the brightening ingredients used with it.
Peels are classified depending on the depth:
– Superficial: There is no light flaking/no downtime; excellent with glow and pigment gradual lifting.
– Medium: A few days of peeling; is directed to older spots of the sun and a little melasma.
– Deep: This is very risky and causes much downtime; pigment is not commonly used in the current practice particularly in dark pigments.
Who gains-and he whom to beware?
Great candidates:
– Sun spots, acne aftermath, lentils.
– Melasma patients who need an enhancement of topical regimens.
– Individuals who are not afraid to recover quickly and work hard to sun protect.
Use caution or avoid:
– Fitzpatrick IV- VI (medium to deep brown) require mild procedures to minimize the threats of post inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH).
– Psoriasis, open lesions, skin infections, or eczematous foci of the skin.
– Pregnancy and breast feeding unless your provider has managed to check it is safe.
– Recent intake of isotretinoin (usually wait 612 months).
– The history of keloids or abnormal scarring is a personal issue that has to be evaluated.
The selection of the appropriate peel to use about your concern.
It has no universal best chemical peel to hyperpigmentation. The perfect fit is dependent on your skin color, sensitivity, and pigmentation type and intensity.
To her acne spots and sunspots:
– Glycolic acid (2035 percent in clinic): Multifunctional AHA that clears the skin and improves complexion.
– Salicylic acid (20-30%): Great on acne prone oily skin and left over pigmentation after acne.
– Modified version of the solution provided by Jessner: A combination that addresses blotchy tone and shallow scarring.
– TCA (10-20 percent): TCA is commonly primarily applied as accurate spot peels three-quarters of small dark spots.
Most of the time, when you are in need of a dark spot chemical peel for pigmentation, the choice options will provide noticeable results in 3 to 6 sessions with 3 to 4 weeks in between.
In sensitive or deeper skin tones (Fitzpatrick IV6)
– Mandelic acid: It is a larger molecule, slows down entry, lower intensity with bright good penetration.
– Lactic acid: moist and mild; excellent route of entry in case easily irritated.
– Weak peels in layers with professional control decrease PIH.
Chemical Peel For melasma
– Melasma is complicated and regressive: A melasma topical peel must be mild and integrated with intense protection of the sun and topical therapy.
– Most appropriate options: NEWS Low-strength glycolic, mandelic based protocols, modified Jessners and careful use of TCA 10-15 percent when necessary.
– Take into account professional depigmentation (e.g. mask-and-cream programs) systems that are specific to melasma.
For under-eye darkness
A chemical peel in dark circles is only effective when the dark pigment is on the surface, and not beneath the surface (bluish/purple) or in the shadows created by hollows and structure.
– Alternatives: Extremely mild lactic or mandelic peels, or make-believe glycolic 20% by an expert. Eye peels should never be done on the DIY.
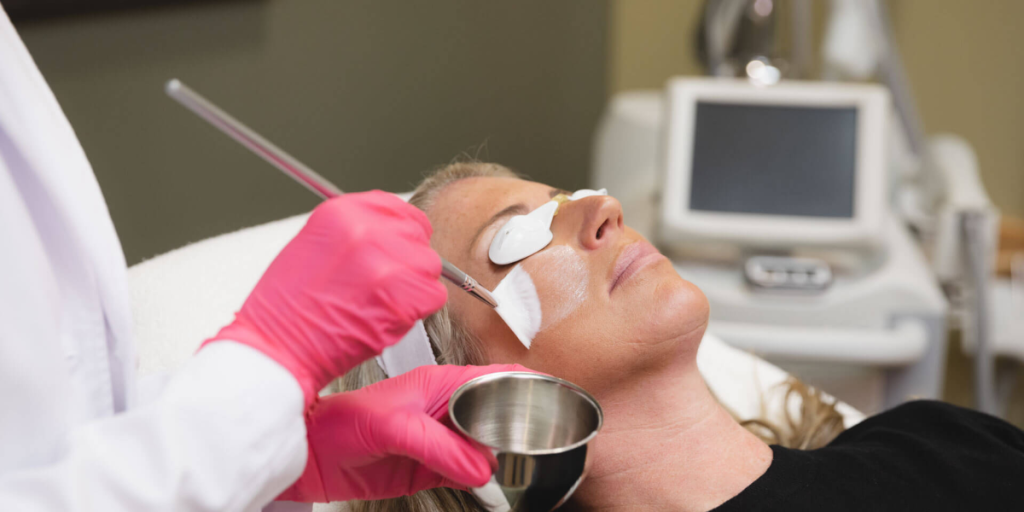
What is the optimal remedy of melasma on face?
Considering the process of managing melasma as a stratified one:
– Sun and heat coverage: SPF 50+, mineral, broad-spectrum, apply after every 2 hours; select it with iron oxides to prevent the appearance of visible light, which will exacerbate melasma. Restrict exposure of heat (saunas, hot yoga).
– Foundation of care (topicals): Hydroquinone (pulses), azelaic acid, kojic acid, vitamin C, niacinamide, tranexamic acid (topical or oral in case of prescription), and retinoids. A time-limited use of a triangular combination (hydroquinone + tretinoin + a weak steroid) is used by many dermatologists.
– Soft, wearable peels: Not a treatment but an addition. Separate them and prevent violate depths which lessen rebound pigmentation.
– Procedural warnings: Not all the lasers can improve melasma. Provided that you take energy-based treatments, ensure that you visit a provider who has worked with melasma and darker skin.
The best treatment for melasma on face is consistent photoprotection plus targeted topicals, with carefully selected peels to accelerate results and maintain clarity.
Expectations of a peel during and after the treatment.
During the Chemical Peel for Pigmentation
– Or you can experience a tingling or a feeling of warmth during some minutes.
– The neutralization or removal depends on the type of peel.
Recovery timeline
– Superficial peels: 2 to 5 days Tightness flaking.
– Medium peels: 3-5–7 days of peeling; schedule downtime.
– Brightening up usually becomes visible after the second or third session.
Session and outcomes of the results.
– Standard: 3-6 courses, 2-4 weeks between.
– Maintenance: After every 23 months when the goals are achieved.
– Melasma needs to be maintained in the long-run; do not expect perfection, just improvement.
Prewear to have safer and more successful results.
– 7 days before peel: Have retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, scrubs and exfoliating acids (unless your provider tells you otherwise).
– In darker complexions or melasma: Your provider can pre-treat with hydroquinone or other brighteners 2-4 weeks prior to initial treatment to decrease the likelihood of PIH.
– 1 week pre-peel: no waxing, threading or hair removal creams.
2 weeks prior No tanning or unprotected sun exposure.
The protection of the progress after peel.
– 50-plus every day; reapply after every 2 hours in the sun. Select mineral/coloured sunscreens that contain iron oxides to treat melasma.
– Clean and moisturize; consider barrier repair. Seek out ceramides, cholesterol, squalane, panthenol or centella.
– Do not take heat, extreme physical activity, and saunas during 4872 hours.
– Take a break on retinoids, acids, vitamin C (when stinging) and exfoliants, 57 days or till healed.
– Snatching off peeling skin is unsafe, so it is better to cut off loose flakes with a sanized scissor.
Safety instructions and side effects.
Common and temporary:
– Erythema, edema, desquamation, slight swellings.
Less common:
– Prolonged redness, acne exacerbation (inquire about prophylaxis in case you have them).
Rare but serious:
– Hyperpigmentation after inflammation (greater risk in deep skin or with harsh peels).
– Scarring, hypopigmentation, infection.
Home peels vs. treatments with the professional level.
At-home options
– Strengths available over the counter are weaker (e.g., glycolic not more than 10, salicylic no more than 2 percent). They are able to preserve tone but will not substitute clinic performance.
– Patch-test and instructions. Under-eye should not be self-peeled.
In-clinic advantages
– More powerful formulaic writings that are more controlled and neutralized.
– Custom made layering to your skin, pigment level and your lifestyle.
– Under-eye and spot-peeling which is safer particularly when using TCA or blended peels.

What is the ideal chemical peel to be used in hyperpigmentation?
It is a matter of cause and skin:
– Acneic marks or oily of the skin: Salicylic or Jessner; glycolic can be used to brighten the skin.
– Sun spots: TCA spot peels, or glycolic series.
– Sensitive or more profound tones: Mandelic or lactic, overlapped.
– Melasma: P.a. glycolic/mandelic or modified Jessner of low strength; peels are used to complement, not to cure.
Tactic mixes that enhance performance.
– Alternating peels with sunscreen daily, vitamin C in the mornings, and an azelaic acid or retinoid at night (resumes actives after recovery).
– To treat melasma or recalcitrant pigment, talk with your provider about short-term use of hydroquinone or topical/ oral tranexamic acid.
– Microneedling or particular lasers should be considered by a professional who behaves specifically in regard to pigmentation and brown complexion.
Cost and timing
– Superficial peels: <|human|>- Superficial peels: usually costing 8800 INR – 22000 INR at a time.
– intermediate or luxury systems: 22000 INR – 53000 INR and above per treatment.
– Prepare a series and maintenance budget in order to safeguard your output.
FAQs
Is hyperpigmentation chemical peel safe on the darker skin?
Yes, with protocol and right peel. Select conservative mandelic, lactic or modified Jessner with choice of pre- and post-care as well as experienced provider.
Will everyone find a chemical peel to dark circles useful?
On condition that the dark circles are predominantly pigmented. Vascular or hollowing causes will not react well with peels; look at fillers, laser to reduce vessels or products that will work on circulation.
What is the difference between a pigmentation and laser treatment with a chemical peel?
Peels lift and shedding The peels may be cheaper and less risky on equipment-related issues. Lasers can penetrate deeper color although it may pose greater PIH risks to darker skin and melasma.
Is a chemical peel used in the treatment of melasma a one-time fix?
No. Melasma is heliophilic, long-term and photophilic. Consider manage and maintain with severe sunscreen, lighteners, and other maintenance peels on a regular basis.
Key takeaways
The personalized approach to the best treatment chemical peel for hyperpigmentation – The peel to the cause, depth, and your skin color.
In melasma, a combination of sun protection and topicals and light, maintenance-based peels is the most appropriate treatment of melasma on face.
Peels under-eye should be non-invasive and administered by the provider.
Long-term clarity is what is locked in by consistency and aftercare and sun-smart habits.
In case you are thinking of having a chemical peel to treat melasma, dark spots or under-eye pigment, schedule an appointment with a trained dermatology specialist. Please come with pictures of your skin in various lightings as well as the names of products you apply. It is all in a customized plan and expectations.
Chemical Peel for Pigmentation at Pyramid Healthcare
At Pyramid Healthcare, we create personalized, skin-first plans to safely and effectively brighten uneven tone and pigmentation. Our experts identify the root cause—such as sun damage, acne marks, melasma, or under-eye discoloration—and match the right chemical peel type and strength to your skin. Options like glycolic, salicylic, or modified Jessner peels fade dark spots over several sessions, while gentler mandelic or lactic peels suit sensitive or deeper skin tones. For true pigment-based dark circles or melasma, we use cautious, professional approaches that combine SPF, brighteners, and mild peels to prevent irritation or rebound. Every treatment includes guidance on aftercare, barrier repair, and sun protection to maintain long-lasting clarity and radiance.
 Skip to content
Skip to content