Skin pigmentation is a natural process, but when it becomes uneven, many people seek ways to lighten or balance their skin tone. Whether caused by sun exposure, hormonal changes, injury, or medical conditions, pigmentation concerns like dark spots and patches can affect self-confidence and skin health. So, the question arises: Can pigmentation treatment device be reduced for a more even complexion? The answer lies in understanding what pigmentation is, why it occurs, and what treatments—both clinical and at-home—are available.
What Is Skin Pigmentation?
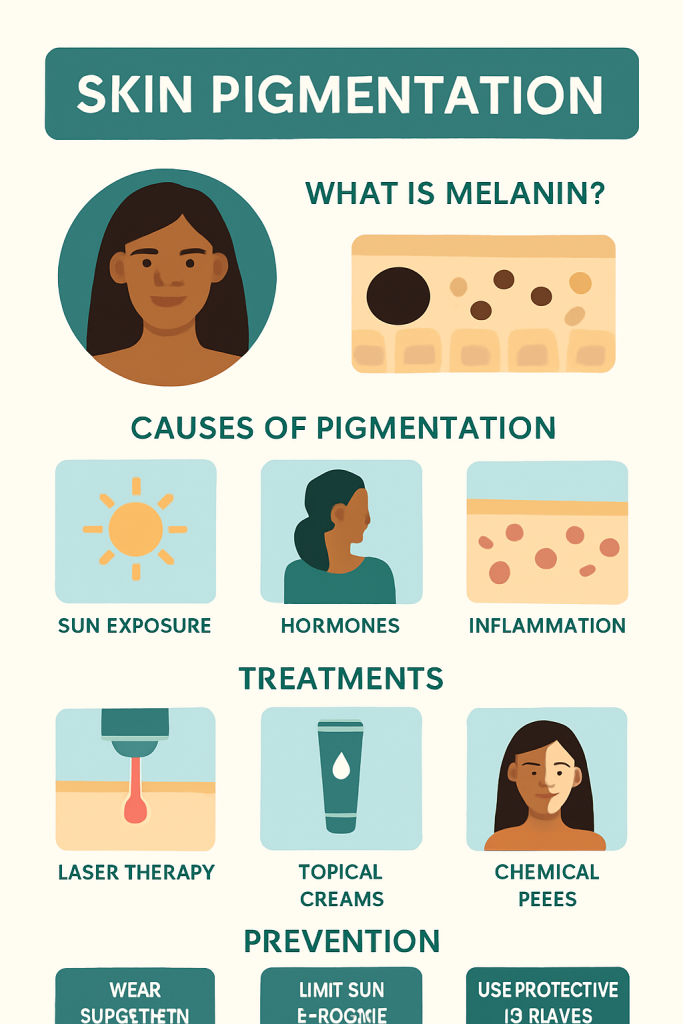
Pigmentation refers to the coloring of the skin, primarily influenced by melanin—the pigment produced by specialized skin cells called melanocytes. Melanin not only determines your natural skin tone but also plays a critical role in protecting your skin from UV radiation.
People with darker skin tones typically produce more melanin. However, pigmentation becomes a concern when melanin accumulates unevenly in certain areas of the skin. This condition, known as hyperpigmentation, leads to spots, blotches, or darkened areas that can result from:
- Prolonged sun exposure
- Hormonal fluctuations (e.g., during pregnancy or due to contraceptives)
- Post-inflammatory responses (e.g., acne scars)
- Medical conditions like melasma
Is It Possible to Reduce Pigmentation?
The good news is yes, pigmentation can often be reduced or faded with appropriate methods. However, results vary depending on the type, cause, and depth of the pigmentation. It’s also important to note that treatment should be approached cautiously to avoid skin damage.
Clinical Treatments to Fade Pigmentation
1. Laser Therapy
Laser treatments target melanin directly and break down pigment clusters in the skin. Some types of lasers remove the outer layer of skin, while others penetrate deeper to stimulate skin renewal.
- Ablative lasers: Remove surface skin layers, helping with deeper pigment issues.
- Non-ablative lasers: Work beneath the skin without damaging the surface, suitable for milder pigmentation.
- Q-switched lasers (e.g., 1064 nm): Specifically designed to target pigment in people with darker skin tones.
Laser treatment should only be administered by a trained professional, especially for people of color, as there is a higher risk of post-treatment pigmentation changes.
2. Intense Pulsed Light (IPL)
Though not technically a laser, IPL uses broad-spectrum light to target pigmented areas. The heat energy breaks down melanin, helping fade sunspots and discoloration. However, IPL is best suited for lighter skin tones and may not be recommended for individuals with deeper complexions.
3. Chemical Peels
Chemical peels use acids—such as glycolic, salicylic, or lactic acid—to exfoliate the top layer of the skin and lighten pigmentation over time. Professional-grade peels penetrate more deeply and may yield faster results, but downtime and potential irritation are common side effects.
Topical Treatments
For those looking for less invasive options, topical treatments are a widely used route to target pigmentation. Many products contain active ingredients that inhibit tyrosinase, an enzyme necessary for melanin production.
Common Ingredients Include:
- Vitamin C: An antioxidant that brightens skin and interferes with melanin synthesis.
- Kojic acid: Derived from fungi, this ingredient can lighten pigmentation and improve tone.
- Retinoids (e.g., tretinoin): Promote cell turnover and encourage the fading of dark spots.
- Azelaic acid: Often used for acne, it also helps reduce pigmentation and inflammation.
- Hydroquinone: A powerful skin-lightening agent, but its use is controversial due to potential side effects. It’s only available by prescription in many countries.
One increasingly popular option is using a retinol face moisturiser that combines hydration with active pigmentation-reducing ingredients. For example, Pure Bubbles Retinol is a formulation that supports skin renewal, helping fade dark spots and even skin tone while moisturizing the skin.
Another effective option for spot correction is an anti hyper pigmentation cream, which specifically targets discolored areas and slows down melanin production. These creams can be used as part of a daily skincare routine for long-term results.
Important: Topical treatments often take weeks to months to show visible improvement and should be used under medical supervision, especially for sensitive or darker skin.
Lifestyle and Prevention: The Role of Sun Protection
Even the most effective pigmentation treatments can be undone without proper sun protection. Sun exposure triggers melanin production, which can worsen existing pigmentation and cause new spots to form.
Here’s how to protect your skin daily:
- Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30 or higher) every day, even indoors.
- Reapply sunscreen every 2 hours when outdoors.
- Wear protective clothing, such as hats and sunglasses.
- Avoid direct sun exposure between 10 a.m. and 2 p.m., when UV rays are strongest.
- Skip tanning beds, which can also accelerate pigmentation.
Prevention is key. Reducing sun exposure helps maintain the results of any pigmentation treatment and prevents new discoloration.
Natural Remedies: Do They Work?
Some individuals turn to natural remedies for managing pigmentation, but scientific support for many of these is limited.
Popular Options:
- Turmeric: Contains curcumin, which may inhibit melanin production.
- Aloe Vera: Rich in compounds like aloesin that might reduce pigment formation.
- Green Tea Extract: Contains EGCG, an antioxidant believed to impact melanin levels.
- Licorice Root: Contains glabridin, which may help lighten dark spots.
- Lemon Juice: High in vitamin C but can be harsh and photosensitizing. Always dilute and avoid sun exposure afterward.
While these remedies are generally safe when used cautiously, they may not deliver dramatic results. Skin irritation or allergic reactions are also possible, so it’s wise to patch-test first or consult a dermatologist.
What About Permanent Solutions?
While it’s possible to fade hyperpigmentation, permanently stopping melanin production isn’t advisable or realistic. Your body will continue to produce melanin as part of its natural defense system.
One compound, monobenzone, has shown permanent depigmenting effects but is generally used only in severe cases of vitiligo and is not recommended for general skin lightening due to the risk of uneven results and increased sun sensitivity.
Risks and Side Effects
Skin lightening treatments come with potential risks, especially when misused or overused:
- Redness, peeling, or irritation
- Allergic reactions
- Paradoxical hyperpigmentation (skin becomes darker)
- Increased sensitivity to sunlight
- Potential long-term damage from harsh products or procedures
Always consult a dermatologist before starting any skin-lightening regimen.
Final Thoughts
Reducing skin pigmentation for a more even complexion is certainly achievable, especially with the right combination of medical treatments, skincare, and preventive habits. Products like Pure Bubbles Retinol, a well-formulated retinol face moisturiser, and a targeted anti hyper pigmentation cream can make a significant difference when used consistently and correctly.
While achieving “perfect” skin may not always be possible, improving tone, texture, and clarity can go a long way in promoting skin confidence and health. And remember—your skin’s natural tone is beautiful. It’s not about changing who you are, but feeling good in the skin you’re in.
If you’re looking for expert guidance and well approved treatments, Pyramid Healthcare offers personalized skin care solutions that blend clinical expertise with modern dermatology. Whether you’re dealing with pigmentation, acne, or dullness, their team can help you find a treatment plan tailored to your skin’s unique needs.
 Skip to content
Skip to content