Advanced Facial Laser Machine Technologies Explained: Q-Switched vs Fractional vs IPL
The modern Facial Laser Machine is no longer a single-function device. Today’s clinics expect platforms that can address pigmentation, scars, wrinkles, vascular lesions, and overall skin rejuvenation—often within the same treatment room. For informed buyers, selecting the right Advanced Facial Laser Machine requires understanding not just indications, but laser–tissue interaction, parameter control, safety profiles, and revenue potential.
This guide breaks down the three core Advanced Facial Laser Machine Technologies—Q-Switched, Fractional, and IPL—through a clinical and commercial lens.
The Physics Behind Facial Laser Machines
All light-based aesthetic devices operate on selective photothermolysis—delivering energy at wavelengths absorbed by specific skin chromophores such as melanin, hemoglobin, or water. The therapeutic effect depends on four critical parameters:
- Wavelength: Determines penetration depth and target
- Pulse duration: Must be shorter than the target’s thermal relaxation time
- Fluence: Controls the amount of thermal or acoustic energy delivered
- Spot size: Influences depth and treatment speed
IPL systems use filtered broadband light, while lasers emit coherent, monochromatic beams, giving them higher precision and predictability.
Q-Switched Laser Technology
Mechanism: Photoacoustic Pigment Fragmentation
Q-Switched systems deliver nanosecond pulses with extremely high peak power, producing a photoacoustic shock wave that fractures pigment particles without significant thermal diffusion.
Typical wavelengths:
- 1064 nm Nd:YAG: Deep dermal penetration, melanin-safe for darker skin
- 532 nm: Superficial epidermal pigmentation
Because melanosomes have thermal relaxation times in the nanosecond range, these ultra-short pulses selectively disrupt pigment while sparing surrounding tissue.
Clinical Use Cases
- Melasma and dermal pigmentation
- Tattoo removal
- Laser toning and carbon peel
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (with low fluence protocols)
Technical Strengths for Buyers
- High safety in Fitzpatrick IV–VI when properly calibrated
- Minimal downtime → high patient turnover
- Strong demand in pigmentation-heavy markets
Practical Limitations
- Multiple sessions required
- Limited collagen remodeling compared to fractional systems
- Recurrence risk in melasma if not combined with medical therapy
Buyer insight: Q-Switched platforms excel as high-volume revenue generators, especially in regions with higher melanin skin types.
Fractional Laser Technology
Mechanism: Micro-Thermal Zones and Collagen Remodeling
Fractional lasers deliver energy in a grid pattern, creating microscopic thermal treatment zones (MTZs) while leaving surrounding tissue intact. These controlled injuries stimulate fibroblast activation, neocollagenesis, and elastin remodeling, leading to long-term skin tightening and resurfacing.
Types Buyers Encounter
- Fractional CO₂ (10,600 nm): Ablative, deep resurfacing
- Er:YAG / Er:Glass (1550–1927 nm): Non-ablative dermal remodeling
MTZs can reach depths of up to 1 mm, enabling treatment of acne scars, wrinkles, and textural irregularities that pigment lasers cannot address.
Clinical Use Cases
- Atrophic acne scars
- Surgical and traumatic scars
- Deep wrinkles and photoaging
- Stretch marks
Technical Advantages
- Adjustable density and energy for customizable depth
- Significant collagen stimulation → long-term outcomes
- Premium treatment pricing and package sales
Trade-offs
- Downtime (especially ablative CO₂)
- Operator skill requirement
- Higher capital investment
Buyer insight: Fractional systems deliver high-ticket, high-margin treatments and position a clinic in the premium anti-aging segment.
IPL Technology
Mechanism: Broadband Photothermal Therapy
IPL devices emit polychromatic light (approximately 400–1200 nm) filtered to target melanin and hemoglobin. Unlike lasers, IPL treats multiple chromophores simultaneously but with less precision.
Clinical Use Cases
- Superficial pigmentation
- Rosacea and telangiectasia
- Photofacial rejuvenation
- Skin tone correction
Technical Strengths
- Large spot size → faster full-face treatments
- Multi-indication platform (pigment + vascular + hair reduction)
- Lower entry cost for new clinics
Limitations
- Less effective for deep dermal lesions
- Greater risk in darker skin without careful wavelength selection
Buyer insight: IPL is ideal as an entry-level Facial Laser Machine for high-throughput rejuvenation services.
Q-Switched vs Fractional vs IPL: Buyer Comparison
| Parameter | Q-Switched | Fractional | IPL |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary target | Pigment | Water (dermal collagen) | Pigment + vascular |
| Energy effect | Photoacoustic | Micro-thermal | Photothermal |
| Depth | Dermal pigment | Adjustable MTZ depth | Superficial–mid dermis |
| Downtime | Minimal | Moderate (CO₂) / Low (non-ablative) | Minimal |
| Best for | Melasma, tattoos | Scars, wrinkles | Tone, redness |
| Revenue model | High volume | High value | High throughput |
What Makes a True Advanced Facial Laser Machine?
An Advanced Facial Laser Machine should offer:
- Multiple wavelengths or handpieces
- Adjustable pulse duration and fluence
- Integrated epidermal cooling
- Preset protocols for different skin types
- Clinical training and service support
Platforms with modular technology allow clinics to expand indications without reinvesting in new hardware, improving long-term ROI.
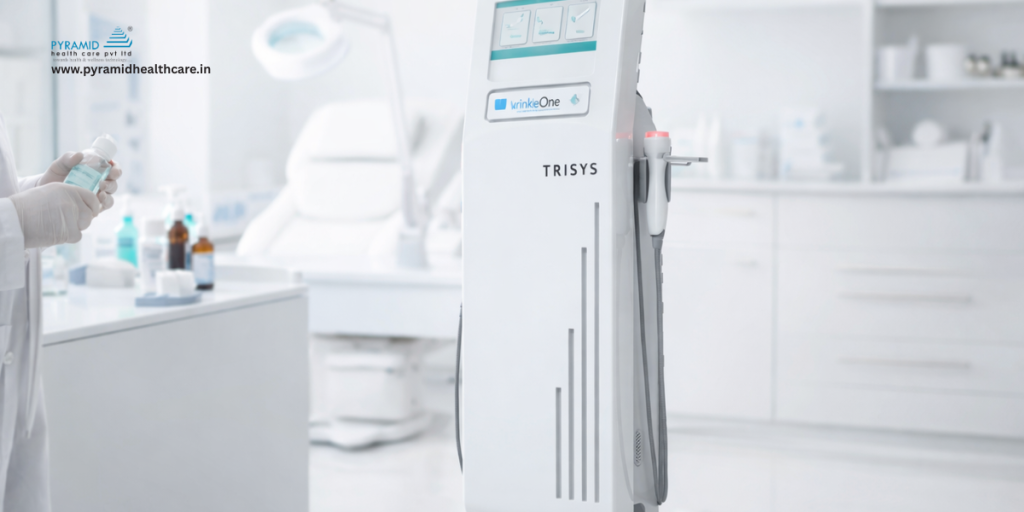
Wrinkle One: A Strategic Non-Surgical Anti-Aging Addition
For clinics looking to strengthen their anti-aging portfolio beyond resurfacing lasers, Wrinkle One provides a focused solution for non-invasive wrinkle reduction and dermal collagen stimulation. By targeting deeper skin layers without ablative damage, it helps improve fine lines, skin laxity, and overall texture while maintaining minimal downtime—an important factor for patient acceptance and repeat sessions. Clinically, it complements fractional and Q-Switched treatments by addressing structural aging rather than only pigment or surface texture, enabling combination protocols that deliver more comprehensive rejuvenation results. From a business perspective, Wrinkle One supports premium anti-aging packages, increases treatment frequency due to its comfort profile, and enhances long-term patient retention—making it a practical addition to any clinic investing in Advanced Facial Laser Machine Technologies.
How to Choose the Right Technology for Your Clinic
Q-Switched if:
- Your patient base has pigmentation concerns
- You treat darker skin types frequently
- You need high-volume, low-downtime services
Fractional if:
- You target acne scars and deep wrinkles
- You operate in a premium anti-aging segment
- You can support downtime and skilled operators
IPL if:
- You want a versatile entry platform
- Your focus is on photofacials and vascular lesions
- Budget is a primary constraint
The Future of Advanced Facial Laser Machine Technologies
Emerging innovations include:
- Picosecond pulse platforms for ultra-precise pigment targeting
- Hybrid laser-RF systems for combined tightening and resurfacing
- AI-guided parameter selection for safer treatments
- Robotic scanning for uniform energy delivery
These developments aim to improve treatment consistency, safety, and operator efficiency, which will be critical for scalable aesthetic practices.
Final Thoughts
Investing in a Facial Laser Machine is a strategic clinical decision—not just a technical one. The most successful clinics align technology with:
- Patient demographics
- Treatment demand
- Operator expertise
- Revenue goals
- Q-Switched: Pigmentation powerhouse
- Fractional: Gold standard for scars and wrinkles
- IPL: Versatile, high-throughput rejuvenation
A well-planned combination of these Advanced Facial Laser Machine Technologies—supported by adjunct devices like Wrinkle One—creates a comprehensive, future-ready aesthetic platform that delivers both clinical excellence and strong financial performance.
Choose the right Facial Laser Machine. Boost results. Grow revenue. Book a demo now.
 Skip to content
Skip to content